Did you know that cocoa butter, also known as theobroma oil, is a pale-yellow, edible fat extracted from the cocoa bean (Theobroma cacao). It’s widely used in producing chocolate, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. An interesting fact about cocoa butter is that it has a melting point just below human body temperature, which allows it to melt smoothly upon contact with the skin, making it a popular ingredient in skincare products.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of cocoa butter, their unique characteristics, and their various applications.
What is cocoa butter?
Cocoa butter is a natural fat extracted from cocoa beans, which are comprised of approximately 50% fat). Cocoa butter is primarily composed of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids, including oleic, stearic, and palmitic acids. This combination of fats contributes to the rich and creamy texture of chocolate. Cocoa butter has a pale-yellow color and is typically stored as a solid slab at room temperature.
The composition and properties of cocoa butter
Cocoa butter is a natural fat extracted from cocoa beans using a heated press. Solid at room temperature, it ranges in color from creamy white to pale yellow, and melts into a clear, golden liquid when warmed above 90°F (32°C). It’s this smooth, creamy fat that gives chocolate its signature melt-in-your-mouth texture.
Key properties:
- Melting Point: Cocoa butter melts between 63–97°F (17–36°C), below human body temperature, allowing it to melt smoothly on the skin and in the mouth.
- Polymorphism: It exists in multiple crystalline forms (Form I–VI), each with a distinct melting point. Form V, or tempered chocolate, is preferred in chocolate making for its glossy finish and satisfying “snap.”
Applications:
- Food Industry: Cocoa butter is essential in chocolate manufacturing, contributing to texture and flavor.
- Cosmetics and Pharmaceuticals: Cocoa butter’s rich emollient properties make it a key ingredient in lotions, creams, and ointments. It deeply hydrates and nourishes the skin, helping to soothe irritation, reduce redness, and smooth rough or sensitive areas.
How cocoa butter is extracted from cocoa beans?
To understand how cocoa butter is extracted, it helps to look at the overall cacao processing journey. Cocoa butter is obtained during the pressing stage, where fat is separated from the ground cacao mass.
- Fermentation and Drying: After harvesting, cocoa beans are fermented and dried to develop flavor and reduce moisture content.
- Roasting: The dried beans are roasted to enhance their flavor and aroma.
- Cracking and Winnowing: Roasted beans are cracked, and the shells are removed, leaving behind the nibs.
- Grinding: The nibs are ground into a thick paste known as cocoa liquor or cocoa mass.
- Pressing: The cocoa liquor is subjected to a heated hydraulic press, which separates the cocoa solids from the cocoa butter.
- Purification: The extracted cocoa butter can be purified to remove any residual solids and odors, resulting in a refined product suitable for various applications.
Types of cocoa butter and their differences
Pressed cocoa butter: Obtained by pressing cocoa liquor (ground cocoa nibs) to separate the fat. Known for its mild flavor and light color, making it suitable for high-quality chocolate production.
Expeller-pressed cocoa butter: Extracted using an expeller press, which mechanically presses the cocoa beans without prior treatment or dehulling. Tends to have a stronger aroma and darker color compared to pressed cocoa butter.
Solvent-extracted cocoa butter: Utilizes solvents, typically hexane, to extract fat from cocoa beans, nibs, or liquor. May have residual solvent traces and a less pronounced cocoa flavor.
Deodorized cocoa butter: Undergoes steam treatment to remove volatile compounds responsible for odors, resulting in a neutral scent.
Ideal for applications such as cosmetics or when a neutral flavor is desired, such as in certain single origin chocolate formulations.
Non-deodorized cocoa butter: Retains its natural aroma and flavor without undergoing deodorization. It preserves the full spectrum of cocoa flavors, which are suitable for products where the distinct cocoa taste is essential.
Natural cocoa butter vs. deodorized cocoa butter
Cocoa butter is typically available in two forms: natural and deodorized. Natural cocoa butter retains its rich scent and flavor, making it ideal for chocolate products with a desired cocoa aroma. It is also minimally processed, helping preserve more nutrients. Deodorized cocoa butter, on the other hand, has a neutral scent and flavor, making it suitable for cosmetics, lotions, and chocolates where a subtle base is needed. It undergoes additional processing to remove the cocoa aroma, which may slightly reduce its nutritional content, but allows other flavors, like in single-origin chocolate, to stand out.
Organic vs. conventional cocoa butter
Organic cocoa butter comes from cocoa beans grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers. It’s often used in natural or eco-friendly products. Conventional cocoa butter is produced using standard farming methods, which may include chemical inputs. The difference mainly lies in how the cocoa is grown and processed.
Food-grade vs. industrial cocoa butter
Cocoa butter is classified into two main types: food-grade and industrial. Food-grade cocoa butter is carefully processed to meet safety standards for consumption, making it suitable for chocolates and other edible products. Industrial cocoa butter, however, is designed for non-edible uses like skincare, cosmetics, and soaps. The key distinction lies in the level of refinement and intended use—only food-grade cocoa butter is safe to eat.
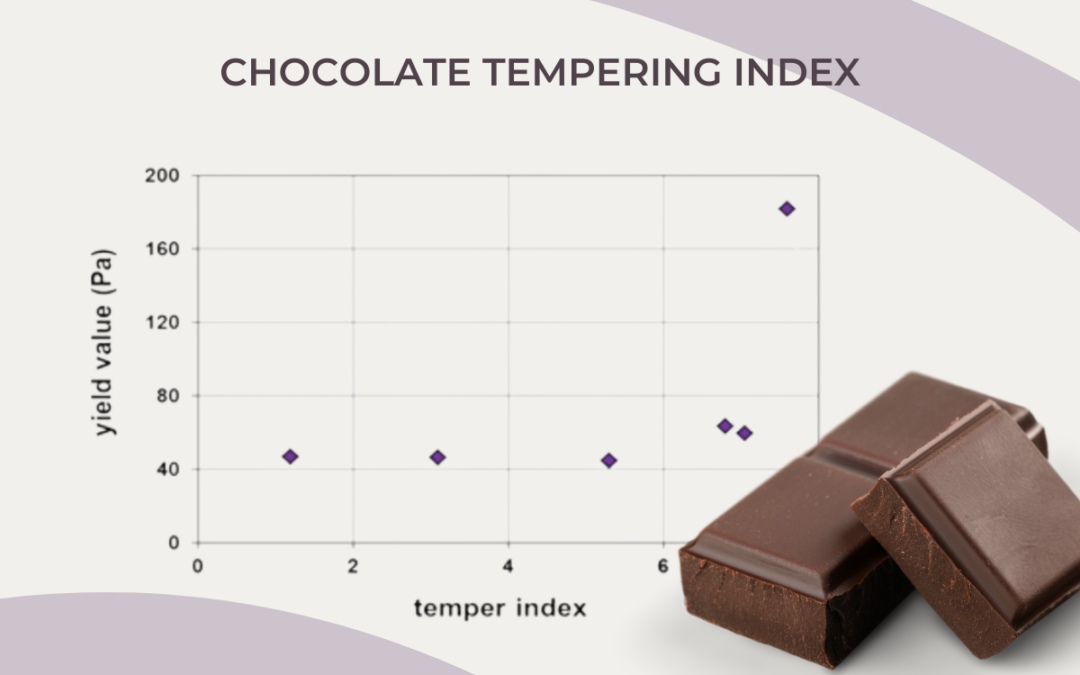
How cocoa butter purity impacts chocolate tempering
Cocoa butter purity refers to how clean and unaltered the fat is—extracted solely from cocoa beans, without any added fats, oils, or impurities. High-purity cocoa butter is essential for successful chocolate tempering, as it directly affects the chocolate’s texture, shine, and snap. Impurities or mixed fats can affect temper temperatures and disrupt crystal formation, leading to issues like fat bloom, poor melting behavior, and a less satisfying mouthfeel.
Here’s what defines cocoa butter purity:
- 100% cocoa fat: No vegetable oils, no fillers, no additives.
- Properly filtered: Free from solids, shells, or unwanted residues.
- Food-grade: Safe for consumption, especially in chocolate-making.
- Deodorized or natural: Either naturally fragrant or lightly processed to remove strong aromas — depending on the desired flavor profile.
Why it matters:
Pure cocoa butter behaves in a predictable, stable way when melted and cooled. That’s essential for:
- Tempering chocolate
- Making smooth textures
- Creating glossy finishes
- Workability
- Ensuring shelf stability
Single-origin vs. blended cocoa butter
Single-origin cocoa butter is cocoa butter made from cacao beans that come from just one specific region, farm, or cooperative. Unlike blends from various places, single-origin cocoa butter has a unique flavor and qualities tied to its specific origin. Factors like the region’s soil, climate, and farming practices shape its distinct taste.
Applications of different types of cocoa butter
Cocoa butter has many uses beyond chocolate. In skincare, it’s prized for its moisturizing benefits and is found in lotions, lip balms, and stretch mark creams. It’s also used in hair care to nourish and smooth dry hair. In cooking, cocoa butter adds a light chocolate flavor and works well in plant-based recipes. Its rich texture makes it ideal for massage products, and it’s even used in pharmaceuticals for its melt-at-body-temperature properties.
We hope you enjoyed this article! If you’re curious to learn more, don’t miss our three in-depth reads on cocoa butter:
- Cocoa Butter 101: All About Cocoa Butter
- The science of chocolate – 6 types of chocolate polymorphs
- Cocoa Butter & Alternatives in Chocolate-Making
- What Is Cocoa Butter Silk?
- How to liquefy cocoa butter
Each one dives deeper into the fascinating world of cocoa butter—check them out!
For more great articles and recipes, check out the rest of our CocoTerra blog.
If you have any questions or comments, feel free to contact us through our social media channels. We are @cocoterra_co on Instagram and Pinterest and @cocoterraco on X (aka Twitter) and Facebook.